In the last post, we talked a lot about the details of the ADS-B signal, but how can we receive the signal and use it to track aircraft in real-time? In this blog, I will show how to use RTL-SDR to build an aircraft tracker.
RTL-SDR
DVB-T dongles based on the Realtek RTL2832U can be used as a cheap SDR since the chip allows transferring the raw I/Q samples to the host. Almost all SDR enthusiasts start from RTL-SDR because of its affordable price. It costs $30 to $40 on Amazone. Although no other SDR can beat its price, you only get what you paid: the performance is very limited. You will find it in the specifications.  RTL-SDR
RTL-SDR
Specifications
- center frequency: 500 kHz to 1.7 GHz.
- outputs 8-bit I/Q-samples.
- up to 3.2 MHz of instantaneous bandwidth (2.4 MHz stable).
- can only be used as a receiver, not a transmitter.
It is not very powerful, so if you want to go professional, get a HackRF or USRP.
Once you received the RTL-SDR
- connect the dongle to the PC and the antenna to the dongle.
- Place the antenna in an open place. Out door will give you the best performance, but indoor by the window will also do the work.
You don’t have to expand the antenna, since you are receiving the GHz signal, which have very short wave length. Read this for more about the antenna.
Software
I assume you have the RTL-SDR dongle and antenna ready. The next step is to install the supporting software. You can find help from the official QUICK START GUIDE. If you are using Linux (why not), Osmocom has a nicely written wiki page for RTL-SDR, and I highly recommend you to go through it for more details.
rtl-sdr
Now, you have Ubuntu installed on your PC or Raspberry Pi, you can use the apt package manager to install the binary files without compiling them.
1
sudo apt install rtl-sdr librtlsdr-dev
Where the rtl-sdr is a packet of primitive tools, and the librtlsdr-dev is the library for making dump1090 in the next step.
rtl_sdris used to record IQ samples to a file or to forward the data to a FIFO. Example: To tune to 392.0 MHz, and set the sample-rate to 1.8 MS/s, use:
1
./rtl_sdr /tmp/capture.bin -s 1.8e6 -f 392e6
rtl_fmallows you to decode and listen to FM/AM/SSB radio. But you will need to installsoxand use sox’splaycommand to play the audio.
1
sudo apt-get install sox
Then you can pipe the output from rtl_fm to play. Note that you can choose your own center frequency -f, and make sure the data rates -r are the same.
1
rtl_fm -f 90.1e6 -M wbfm -s 200e3 -r 48e3 - | play -r 48e3 -t s16 -L -c 1 -
A few more applications, such as police scanner, airband scanner, and pager decoder can be found here.
rtl_adsbis a simple ADS-B decoder, maybe too simple. It can only demodulate the ADS-B message into HEX format. See the screen below. If you are satisfied with this result, you can stop here now, but if you like to have rich information and even a map with live aircraft locations, let’s continue.
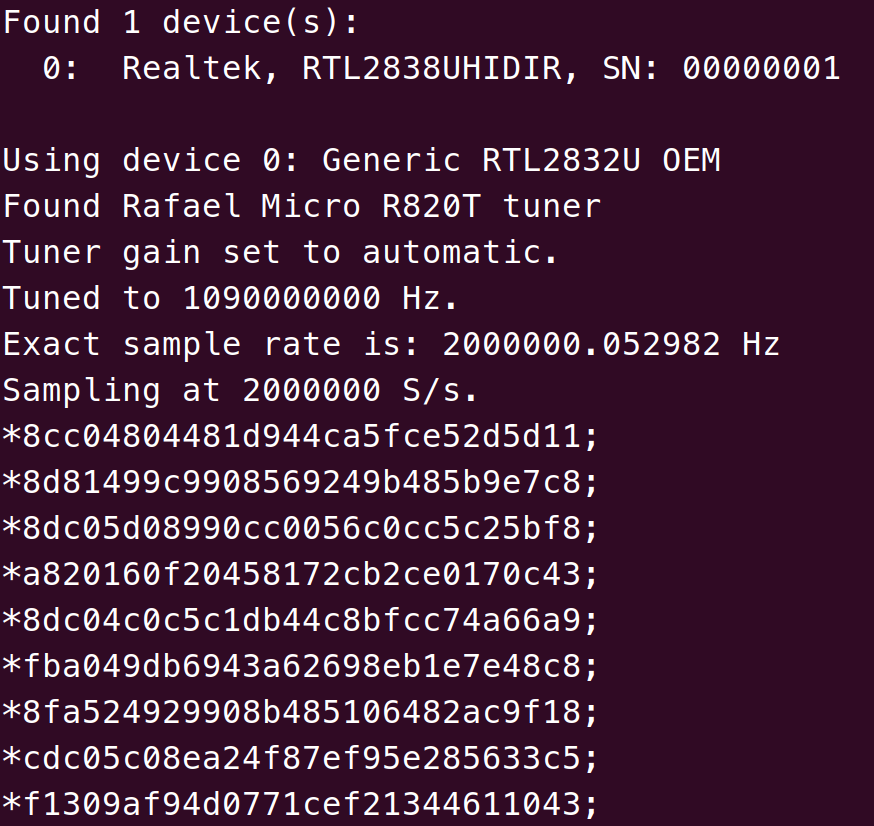
I will only list three tools, please refer to the Osmocom wiki page for more.
There is also a Python library, pyrtlsdr for RTL-SDR development.
dump1090
Dump 1090 is a Mode S (ADS-B) decoder specifically designed for RTLSDR devices.
To install it, you will need to compile it from the source code. I know that isn’t pleasant for many users, just get used to it.
1
2
3
git clone https://github.com/antirez/dump1090.git
cd dump1090
make
To run the program in interactive mode, with networking support, and connect with your browser to http://localhost:8080 to see live traffic:
1
./dump1090 --interactive --net
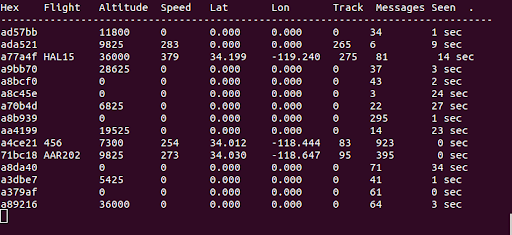
You can find a more readable table in the terminal.
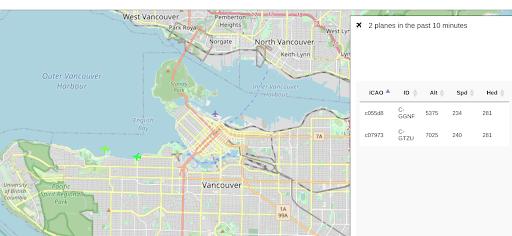
Also, there is a live air traffic map in your browser. Note that the screenshot below is from Kismet, but they are generally similar.
Thanks for reading.
Comments powered by Disqus.